Since its advent in the 1960s, laser technology has rapidly developed into a key tool in the field of industrial manufacturing due to its high energy density, good directionality and controllability. Compared with traditional mechanical processing methods, laser processing has significant advantages such as non-contact, high precision and high degree of automation, and is widely used in industrial manufacturing such as material cutting, welding, marking, drilling and additive manufacturing. According to the type of laser and its process characteristics, industrial laser processing is mainly divided into three categories: laser cutting, laser welding and laser additive manufacturing. Each process method has its unique mechanism of action and application scope.
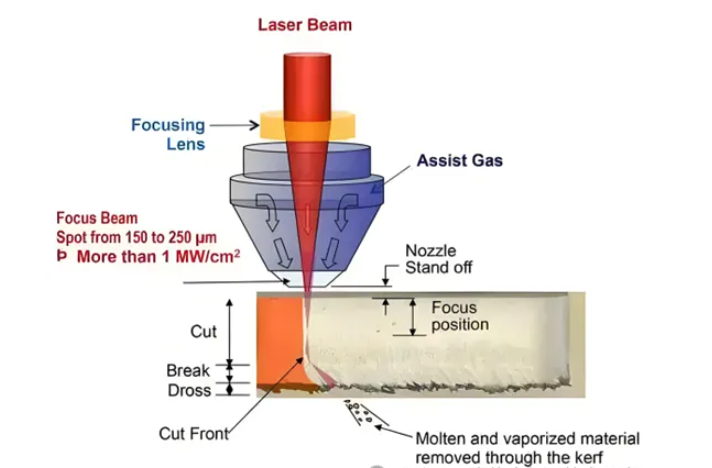
Laser cutting is one of the most mature industrial laser applications. It uses a high-power laser beam to melt and vaporize materials, and is combined with auxiliary gas to blow away the slag, achieving efficient and precise cutting. CO₂ lasers and fiber lasers are currently the mainstream equipment, suitable for cutting medium and thin plates of materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy. The advantages of this technology lie in its narrow slit, small heat-affected zone, no need for molds and the ability to quickly change processing paths. It is particularly suitable for high-demand industries such as automotive manufacturing, sheet metal processing and aerospace.
In automotive manufacturing, laser cutting is used to produce various components ranging from body panels to engines. For instance, fiber lasers are used for high-precision cutting of high-strength steel components, thereby achieving the lightweighting of automobiles.
(2) The aerospace industry also benefits from laser cutting technology, especially in the production of complex components made of advanced materials such as titanium and composite materials. For instance, ultrafast lasers can be used to cut titanium alloy components with complex shapes, while minimizing thermal damage and ensuring the structural integrity of the components, significantly enhancing the performance and safety of aerospace components.
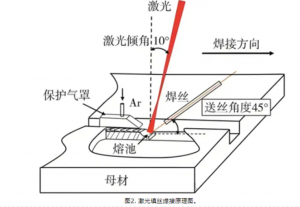
Laser welding achieves connection by rapidly melting metal materials with a laser beam, featuring deep penetration, high speed, and low heat input. Common welding modes include continuous laser welding and pulsed laser welding, which are suitable for thin plate precision welding and deep penetration welding scenarios. Compared to arc welding, laser weld seams have higher strength and less deformation, and are applicable in fields such as battery packaging, stainless steel component welding, and nuclear power structural component manufacturing. Particularly in battery manufacturing, laser welding has become the mainstream connection method.
(1) In the automotive industry, laser welding is used to connect body panels, engine components, and other critical parts. For example, fiber lasers are used for high-precision welding of high-strength steel components to form strong and durable joints.
(2) In the electronics industry, laser welding is used for high-precision connection of small and precise components. For instance, diode lasers are used to weld battery cells in lithium-ion batteries to ensure the reliability of electrical connections.
(3) In the aerospace industry, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner uses laser welding technology to connect titanium alloys and composite materials, significantly reducing the number of rivets, lowering the fuselage weight, and improving fuel efficiency.
Laser technology, as an important pillar of advanced manufacturing, is constantly expanding its industrial application boundaries. Currently, laser processing is also developing towards higher power, higher precision and multi-process integration directions, such as laser-electric arc composite welding, laser ultrafast micro-processing, and laser intelligent monitoring systems. In the future, with the continuous advancement of high-power semiconductor lasers, intelligent control systems, and green manufacturing concepts, laser processing will continue to play a key role in intelligent manufacturing, personalized products, and extreme material processing fields.
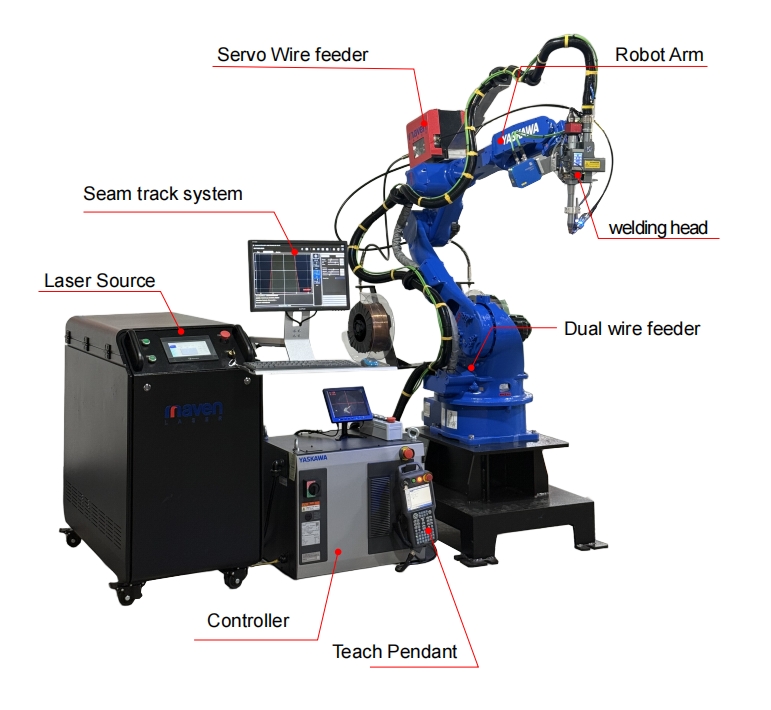
ROBOT LASER WELDING MACHINE——PROFESSIONAL WELDING SOLUTION
★ Wire Feeder and Welding Concentrated on the Control Pedal
★ 0.08mm Robot Positioning Accuracy
★ Raycus Max JPT IPG Laser Source Optional
★ Customization of Whole System
Post time: Apr-25-2025