Laser: Definition, Industrial Chain, Applications, and Global Landscape
Laser refers to light produced by the stimulated emission of atoms, hence the name “laser”. Since the 20th century, laser has been another major invention of humanity following nuclear energy, computers, and semiconductors, and is known as the “fastest knife”, “most accurate ruler”, and “brightest light”. Its applications are extremely extensive, including laser marking, laser welding, laser cutting, optical fiber communication, laser ranging, laser radar, laser weapons, laser discs, laser vision correction, laser cosmetology, laser scanning, laser mosquito killers, and Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) non-destructive testing technology.
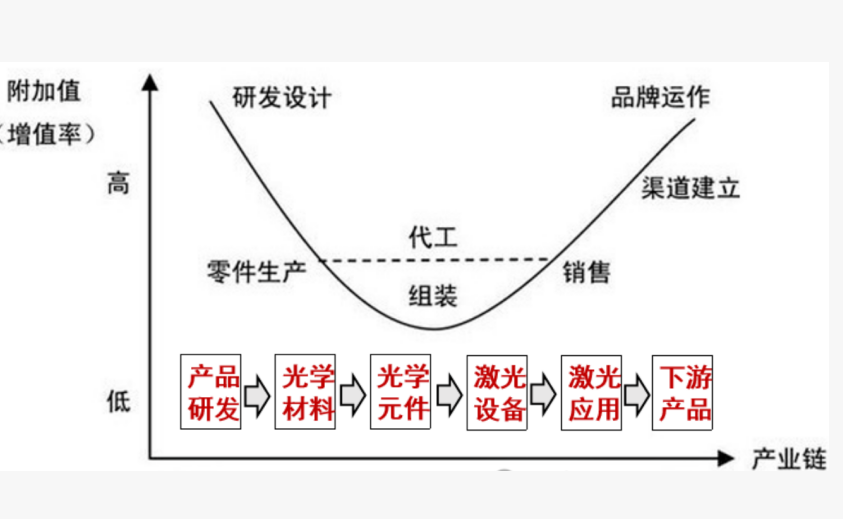
Laser Industry Chain
The laser industry is a comprehensive high-tech industry centered on laser technology, covering laser material research and development, device manufacturing, system integration, and end-user applications. It revolves around the generation, control, transmission, and application of lasers, involving a complete industrial chain from basic materials to end products.
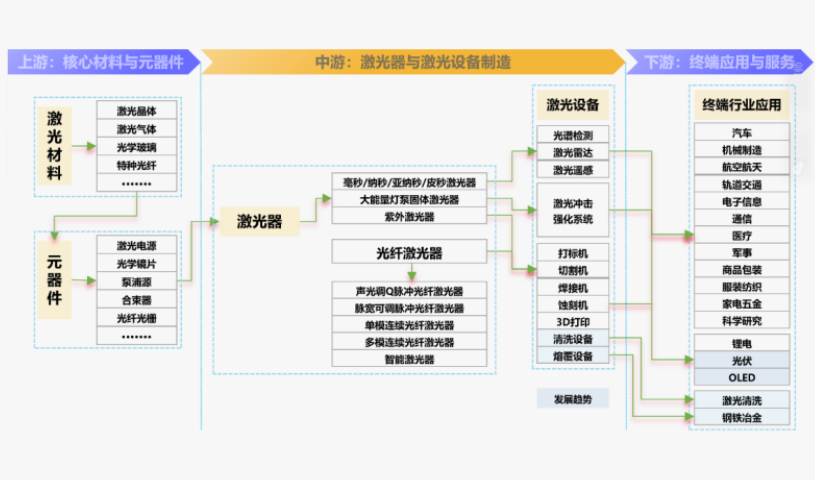
Upstream of the Industrial Chain
It mainly includes the production and sales of laser materials and supporting components. These materials, which form the foundation of laser equipment, consist of laser crystals, laser gases, laser lamps, and laser power supplies. Additionally, it encompasses relevant production auxiliary materials such as optical lenses, pump sources, galvanometers, and gratings. The quality and performance of these materials and components directly impact the quality and performance of laser equipment.
Midstream of the Industrial Chain
This segment is primarily engaged in the manufacturing and sales of various lasers, as well as laser supporting equipment like numerical control devices and computers. Lasers are the core components of laser equipment, with diverse types including solid-state lasers, semiconductor lasers, and fiber lasers. The midstream also involves integrating and packaging upstream laser chips, optoelectronic devices, modules, and optical components to produce various laser equipment such as laser cutting machines, laser welding machines, and laser marking machines.
Downstream of the Industrial Chain
It represents the application fields of laser equipment, covering numerous sectors such as advanced manufacturing, healthcare, scientific research, automotive applications, and information technology. For instance, laser cutting machines can be used for cutting metal materials, laser welding machines for welding automotive parts, and laser marking machines for marking product labels. In these fields, laser equipment plays a crucial role in driving the development and progress of related industries.
Advantages and Major Application Fields of Laser Technology
Laser technology, with its advantages of high precision, high efficiency, and non-contact operation, is playing an increasingly important role in strategic emerging industries:
- In the field of new-generation information technology, it supports the development of new display and communication sectors, driving innovations in information technology.
- In the high-end equipment manufacturing field, it enhances the level of green manufacturing and intelligent manufacturing, empowering the development of high-speed railways and instrumentation.
- In the new energy sector, it promotes the development of high-efficiency solar energy and smart grids, accelerating the application of new energy.
- In the new materials field, it enables precise material processing, providing strong support for new material research and development.
- In the new energy vehicle industry, it optimizes the processing and welding of automotive parts, advancing the upgrading of the new energy vehicle industry.
- In the energy conservation and environmental protection field, it is applied in semiconductor lighting, contributing to the progress of the energy conservation and environmental protection industry.
- In the biological industry, it improves the performance of advanced medical equipment, driving innovation in the biological industry.
However, overall, the most widespread applications of lasers remain in material processing and communication.
Global Laser Industry Pattern
- European Countries: They took an early lead in laser technology and have accumulated profound technical expertise, holding advantages in high precision, high reliability, and high-end market applications (e.g., semiconductor and lithography technology). According to market research data, Europe’s laser industry accounts for over 30% of the global market share.
- The United States: It occupies an important position in the global market in fields such as high-end optical chip design and silicon photonics integration technology. In particular, IPG Photonics leads the global fiber laser market. Overall, the U.S. laser industry holds nearly 20% of the global market share.
- Japan and South Korea: They have unique strengths in precision manufacturing, optical technology, and applications in some niche segments. For example, Japan leads the world in optical fiber preforms and special optical fibers, with a global market share exceeding 50%; South Korea’s Meere Company holds 70% of the global market share in display edge grinders. However, accurate data on the overall global market share of Japan and South Korea’s laser industries is difficult to obtain.
- China: It has distinct advantages in laser equipment manufacturing and dominates the global market in this field. In 2024, the global laser equipment market revenue was approximately 21.8 billion U.S. dollars, among which China’s laser equipment market revenue reached 89.7 billion yuan (accounting for 56.6% of the global market). Nevertheless, when considering the entire industrial chain (including core materials and components, high-end laser equipment manufacturing, and advanced applications), China’s market share decreases to approximately 21% of the global total.
Development of China’s Laser Industry
Policy Support
The Chinese government attaches great importance to the development of the laser industry and has introduced a series of supportive policies to promote the R&D, industrialization, and market expansion of laser technology.
Regional Industrial Clusters
Currently, China has a large number of enterprises in the laser industrial chain, and regional industrial competition is fierce. The main industrial clusters are as follows:
- Wuhan Optics Valley: By deeply integrating technological innovation and industrial innovation, it has built a highland for the development of China’s laser industry. It gathers over 200 laser enterprises, covering various gas, solid-state, and fiber laser enterprises with high, medium, and low power. A complete industrial chain has been formed, encompassing upstream laser materials and supporting components, midstream lasers and supporting equipment, and downstream laser applications.
- Pearl River Delta: Driven by market demand, it stimulates the industrial demand for laser manufacturing and promotes the improvement of all links in the industrial chain. As the largest application market for China’s laser industry, its export volume accounts for over 30% of the national total. The industrial scale of this region is approximately 13 billion yuan, making it the second-largest laser industry cluster in China after Wuhan.
- Bohai Rim: It boasts strong technological R&D capabilities and robust market demand. Represented by Beijing, this market gathers a large number of enterprises in the IT and communication industries, generating strong demand for laser products.
- Yangtze River Delta: It has a relatively complete industrial chain, with industries mainly distributed in Shanghai, Nanjing, Wenzhou, Suzhou, Ningbo, and other cities. The laser industry in this region is characterized by cross-regional collaborative innovation, driving the quality and efficiency improvement of the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain through leading enterprises. The number of patent applications in core technology fields such as ultrafast lasers and high-precision galvanometer systems in the Yangtze River Delta increases by an average of 34% annually, and the technology conversion rate is significantly higher than the national average.
As China’s largest laser industry base, Wuhan Optics Valley is home to more than 300 laser-related enterprises, with a total revenue exceeding 20 billion yuan. The annual output value of laser processing products accounts for one-third of the national total. It demonstrates significant advantages in talent, technology, industrial foundation, and market:
- Talent Advantage: Around 18 institutions of higher learning and 56 provincial and ministerial-level scientific research institutes are concentrated around the base, cultivating over 50,000 college students annually, providing abundant talent resources for the laser industry.
- Technological Advantage: Institutions such as Wuhan Research Institute of Posts and Telecommunications and Huazhong University of Science and Technology are at the domestic leading level in optical communication technology and laser processing, offering strong technical support for industrial development.
- Industrial Foundation Advantage: Wuhan Optics Valley has developed into China’s largest optical fiber and cable manufacturing base and laser equipment production base, with a solid industrial foundation.
- Market Advantage: The base holds a large share in the domestic optical fiber and cable product market and optoelectronic device market, and also occupies a certain position in the global optoelectronic industry, boasting broad market prospects.
Market Dynamics and Core Components of Laser Equipment
Market Dynamics of Laser Equipment
Laser equipment is a typical general-purpose equipment, with its downstream widely distributed in industries such as automotive, 3C (computer, communication, consumer electronics), sheet metal, and shipbuilding. The industry’s prosperity is highly correlated with the macroeconomy, and its cyclical fluctuations are basically consistent with the macro cycle of the manufacturing industry. In recent years, the decline in laser prices has led to a reduction in equipment prices, improving the economic efficiency of laser equipment and accelerating the industry’s penetration rate.
Key downstream application trends:
- Lithium Battery Production: Lasers are widely used in lithium battery production. Lithium-ion batteries have high requirements for safety, consistency, and density, and laser processing has obvious advantages in processing effect and efficiency. Currently, with the rapid development of new energy vehicles, the demand for lithium battery equipment is strong, and lithium battery enterprises are expanding their production capacity. Given the widespread application of laser cutting, cleaning, and marking in lithium battery manufacturing, the proportion of laser processing equipment in power lithium battery manufacturing is expected to reach 15-20% in the future.
- Laser Cleaning and Laser Cladding: These emerging application markets have broad prospects. Compared with chemical cleaning and mechanical grinding, laser cleaning is environmentally friendly, non-damaging, free from secondary pollution, and efficient. It can replace existing markets such as industrial cleaning and manual polishing, with huge market potential. Newly developed application fields include cultural relic cleaning, building cleaning, and street cleaning.
- Photovoltaic Industry: Laser processing technology can significantly improve the efficiency of photovoltaic cells. Driven by favorable factors such as the continuous decline in photovoltaic power generation costs and the demand from emerging markets, the global photovoltaic market will continue to grow. Laser processing is applied in processes such as ablation, cutting, edge trimming, and doping in solar cell production.
Core Components of Lasers
- Cost Structure: From the cost structure of lasers, special optical fibers, pump sources, and optical devices are the main cost components, accounting for over 80%. Among them, pump sources and special optical fibers are the core sources of raw material costs for fiber lasers—generally, special optical fibers account for approximately 20%, and pump sources account for approximately 30%.
- Key Tracking Indicator: When analyzing the core components of lasers, the most important indicator is the degree of self-production (or localization) of these core components. A higher proportion of self-production (or localization) leads to a faster decline in procurement costs.
- Pump Sources: As the light source of fiber lasers, pump sources are used to excite the laser working medium and pump the active particles from the ground state to a higher energy level to achieve population inversion. According to the differences in working media and laser operating conditions, they are divided into four types: optical excitation (optical pumping), gas discharge excitation, chemical excitation, and nuclear energy excitation. The corresponding types of lasers are fiber lasers, carbon dioxide lasers, solid-state lasers, etc.
- Special Optical Fibers: The core feature that distinguishes special optical fibers from ordinary optical fibers is their use at specific wavelengths. Ytterbium-doped fibers are used as gain media for fiber lasers and fiber amplifiers, while passive fibers are used for couplers, pigtails, and other optical devices.
Future Development Trends of the Laser Industry
As laser technology deeply integrates with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, and with the continuous emergence of new lasers like ultrafast lasers and high-power fiber lasers, the laser industrial chain will develop to a higher level, bringing revolutionary changes to fields such as material processing and biomedicine.
Meanwhile, as the global manufacturing industry moves toward intelligence and greenization, laser manufacturing, with its advantages of high precision and strong adaptability, will accelerate its penetration into precision manufacturing fields such as display panels, consumer electronics, and integrated circuits, further expanding its application market.
In addition, the continuous support of national policies for the laser industry and the relevant policies introduced by local governments will lay a solid foundation for the improvement and expansion of the laser industrial chain, promoting the laser industry to develop in the direction of higher quality and higher efficiency.
Post time: Sep-03-2025