Laser Arc Composite Welding Technology
Introduction to Laser Arc Composite Welding Technology
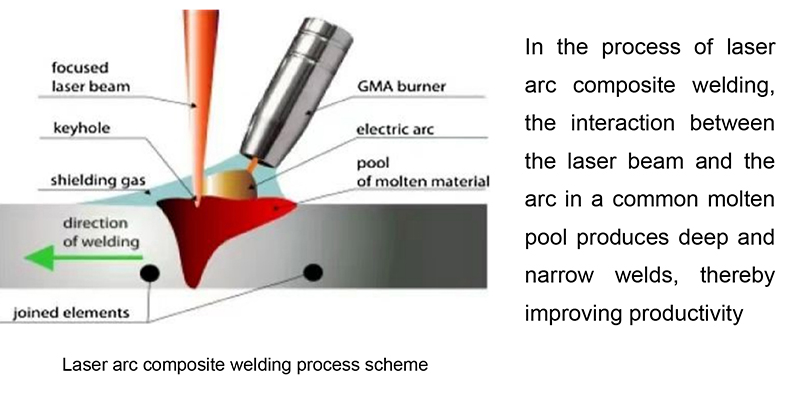
Laser arc composite welding technology is a welding method that uses laser and arc as dual heat sources, acting on the same molten pool to form laser guided and stable arc. The arc improves the metal's absorption rate of laser.
Basic principles of laser arc composite welding
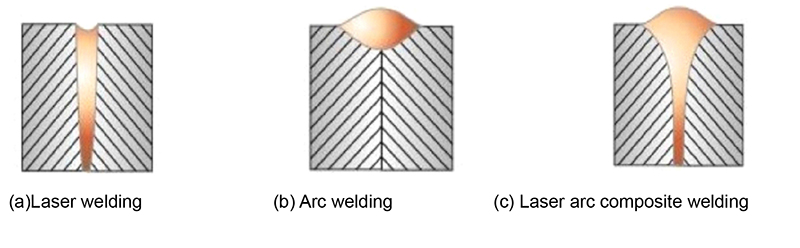
Laser welding is known for its very narrow heat affected zone and the ability to focus the laser beam on a very small area to produce narrow and deep welds, which can achieve higher welding speeds, reduce heat input, and lower the probability of thermal deformation of welded parts. However, the gap bridging ability of laser welding is poor, so high precession is required in workpiece assembly and edge preparation. Laser welding is very difficult for welding high reflectivity materials such as aluminum, copper, and gold. On the contrary, arc welding technology has excellent gap bridging ability, high electrical efficiency, and can effectively weld materials with high reflectivity. However, the low energy density during arc welding can slow down the welding process, resulting in a large amount of heat input in the welding area and causing thermal deformation of the welded parts. Therefore, while using high-power laser beams for deep welding, the synergistic effect of arc with high energy efficiency is employed, and its mixed effect compensates for the defects of the process and supplements its advantages.
Advantages of Laser Arc Composite Welding Process
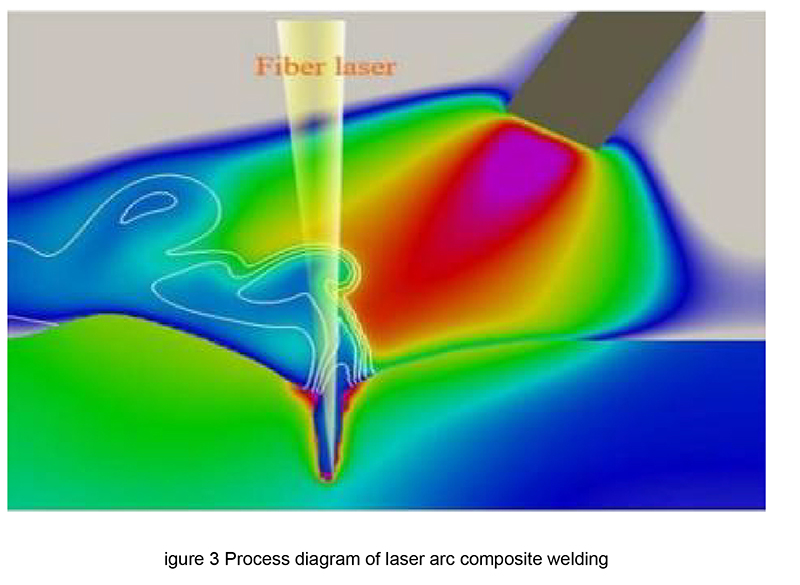
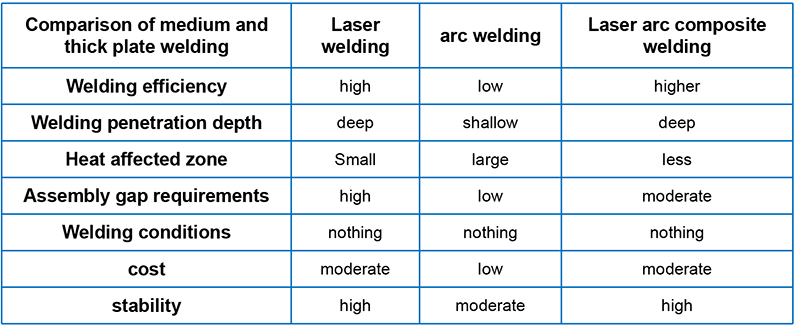
The disadvantage of laser welding is poor gap bridging ability and high requirements for workpiece assembly; The disadvantage of arc welding is that when welding thick plates, it has low energy density, shallow melting depth, and generates a large amount of heat input in the welding area, which can lead to thermal deformation of the welded parts. The combination of the two can mutually influence and support each other, and compensate for the defects of each other's welding processes, fully utilizing the advantages of laser deep penetration and arc welding cover, achieving the advantages of small heat input, small weld deformation, fast welding speed, and high welding strength, as shown in Figure 3. The comparison of the welding effects of laser welding, arc welding, and laser arc composite welding on medium thick plates is shown in Table 1.
Comparison of Welding Effects of Medium and Thick Plates
Technical features
— High efficiency: Laser welding has fast speed, concentrated heat input, and improves production efficiency.
— Large aspect ratio: Laser welding can achieve a large aspect ratio, suitable for welding complex structural components.
— Small heat affected zone: Laser welding has a smaller heat affected zone, reducing the impact on material properties.
— High flexibility: can adapt to welding requirements of different materials and shapes.
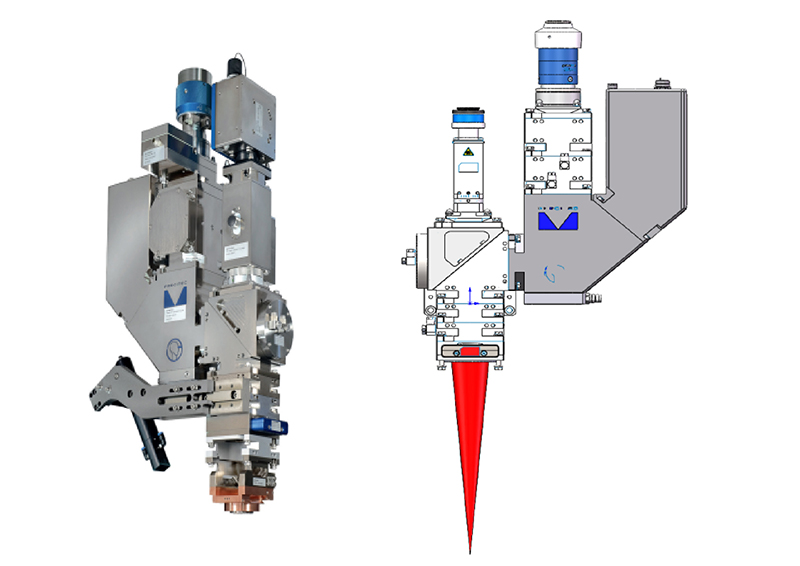
Laser welding head
Efficient
— High dynamic spot position
— The width of the weld seam can be adjusted according to the wiping gap
— Welding with a gap of 0.4mm that can be loosened and overlapped
— Flexible control of laser power
— Used in different welding applications
Flexible
— Can be applied in welding, cladding, and fire applications
— Used for all conventional welding geometric surfaces
— Simultaneously perform spot oscillation and weld seam tracking
— Directly transmit data with PLC
— Independently used as an independent solution or in conjunction with the WeldMaster platform
Easy to use
— Easy to operate
— Only one computer is needed for system configuration
— Simple operation interface
— Can monitor the control status
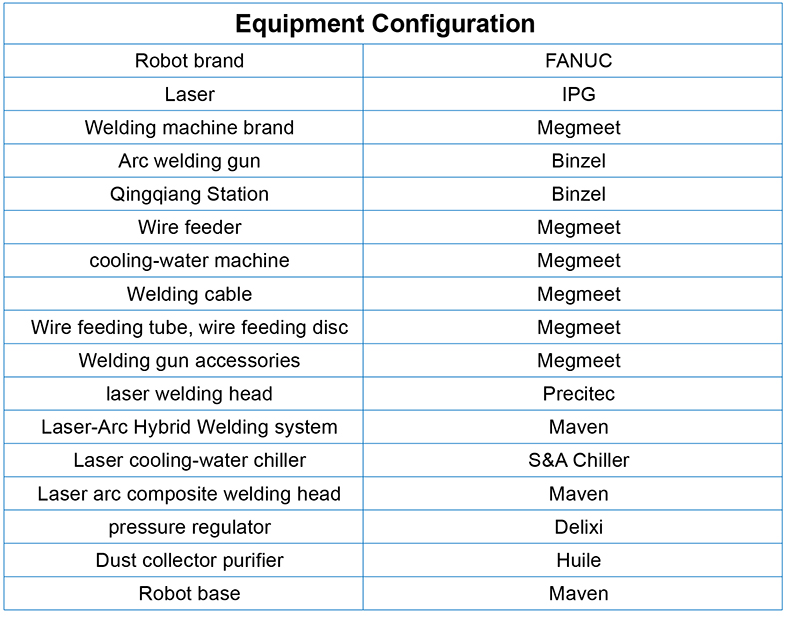
Equipment Configuration